Sleep apnea
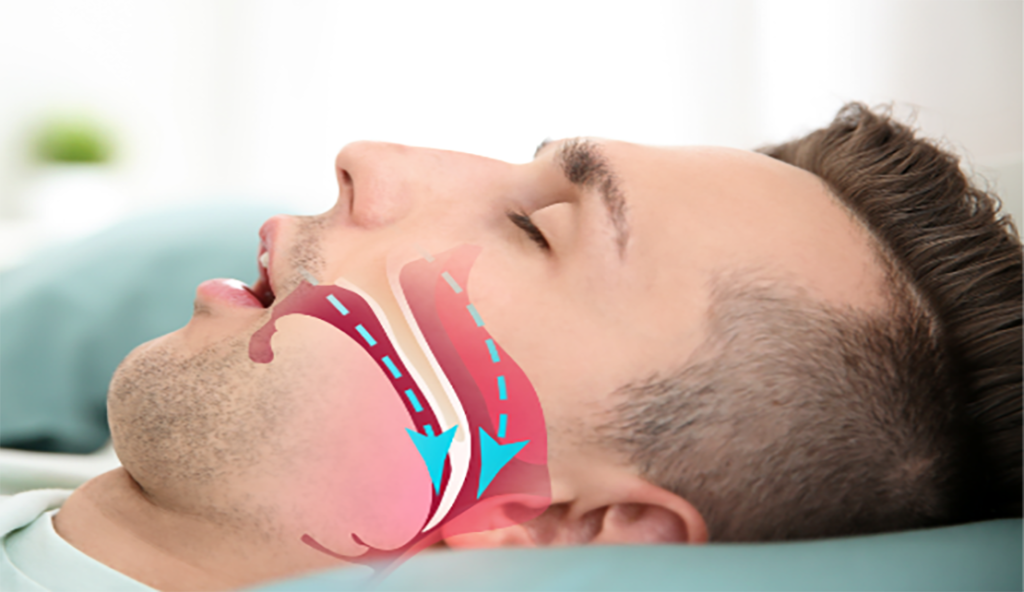
Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts. If you snore loudly and feel tired even after a full night’s sleep, you might have sleep apnea.
Definitions:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea occurs when breathing is interrupted during sleep.
- Central Sleep Apnea occurs when your brain doesn’t send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome, also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, occurs when someone has both obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea
Symptoms:
The signs and symptoms of obstructive and central sleep apneas overlap, sometimes making it difficult to determine which type you have. The most common signs and symptoms of obstructive and central sleep apnea include:
- Loud snoring
- Episodes in which you stop breathing during sleep — which would be reported by another person
- Gasping for air during sleep
- Awakening with a dry mouth
- Morning headache
- Difficulty staying asleep (insomnia)
- Excessive daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia)
- Difficulty paying attention while awake
- Irritability
- Daytime fatigue
You might have difficulty concentrating and find yourself falling asleep at work, while watching TV or even when driving. People with sleep apnea have an increased risk of motor vehicle and workplace accidents.
You might also feel quick-tempered, moody or depressed. Children and adolescents with sleep apnea might perform poorly in school or have behavior problems.
Medical Issues Associated with Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea might also increase your risk of recurrent heart attack, stroke and abnormal heartbeats, such as atrial fibrillation. If you have heart disease, multiple episodes of low blood oxygen (hypoxia or hypoxemia) can lead to sudden death from an irregular heartbeat.
- High blood pressure or heart problems. Sudden drops in blood oxygen levels that occur during sleep apnea increase blood pressure and strain the cardiovascular system. Having obstructive sleep apnea increases your risk of high blood pressure (hypertension).
- Type 2 diabetes. Having sleep apnea increases your risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolic syndrome. This disorder, which includes high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, high blood sugar and an increased waist circumference, is linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
- Complications with medications and surgery. Obstructive sleep apnea is also a concern with certain medications and general anesthesia. People with sleep apnea might be more likely to have complications after major surgery because they’re prone to breathing problems, especially when sedated and lying on their backs.
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Attention Deficit
Did You Know ?
Approximately 38% of the general population has a type of orofacial myofunctional disorder.

